Dave Drohan (SETU)
Add Spot
In Spot, we have hard-coded the values for xCoord, yCoord and diameter in the default constructor:
private float xCoord;
private float yCoord;
private float diameter;
public Spot() {
xCoord = 100;
yCoord = 200;
diameter = 40;
}
Now add a second Spot constructor that will allow us to read in the values for these fields from the Driver class:
public Spot(float xCoord, float yCoord, float diameter) {
this.xCoord = xCoord;
this.yCoord = yCoord;
this.diameter = diameter;
}
Testing new constructor
Let’s test this constructor from the Driver, before we start allowing the user to type in values from the console for Spot.
To do this, return to Driver and do the following:
remove this line from the Driver constructor:
spot = new Spot();
and update the Spot declaration:
Spot spot;
with
Spot spot = new Spot(40, 43, 22);
When you run the app, are the new values that you entered into the constructor displayed on the console:
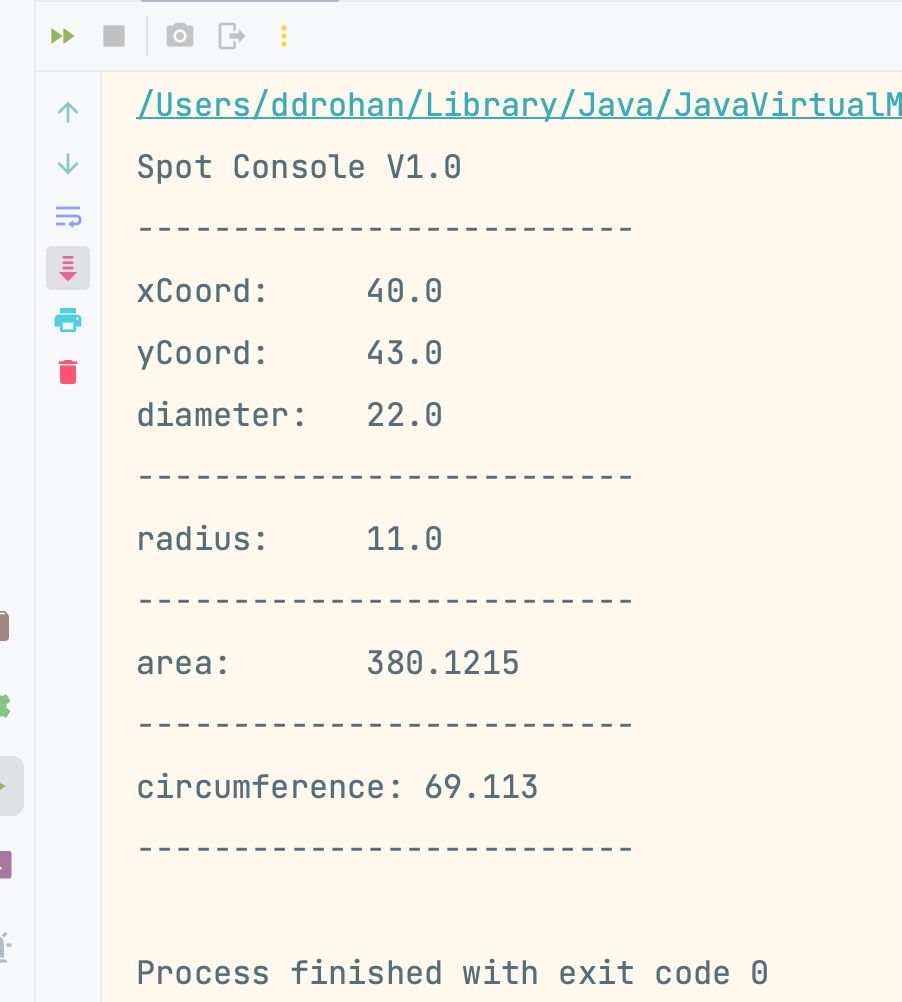
Asking the user for the values
Now we will update the Driver class so that we can ask the user to enter the values for this new constuctor, rather than us hardcoding the value like above.
In Driver, add the following new field, just below the Spot variable declaration, if you haven’t done so already:
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
It will give you a syntax error if you are missing the following import:
import java.util.Scanner;
so add that now if necessary.
Still in Driver, add the following new method:
void addSpotDetails(){
System.out.print("Enter xCoord value: ");
float enteredXCoord = input.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Enter yCoord value: ");
float enteredYCoord = input.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Enter diameter value: ");
float enteredDiameter = input.nextFloat();
spot = new Spot(enteredXCoord, enteredYCoord, enteredDiameter);
}
and call it as the first method in the Driver() constructor i.e.:
Driver(){
addSpotDetails();
drawSpot();
printRadius();
printArea();
printCircumference();
}
Run the app
Now run the app and you should be asked to enter in values for the spot fields:
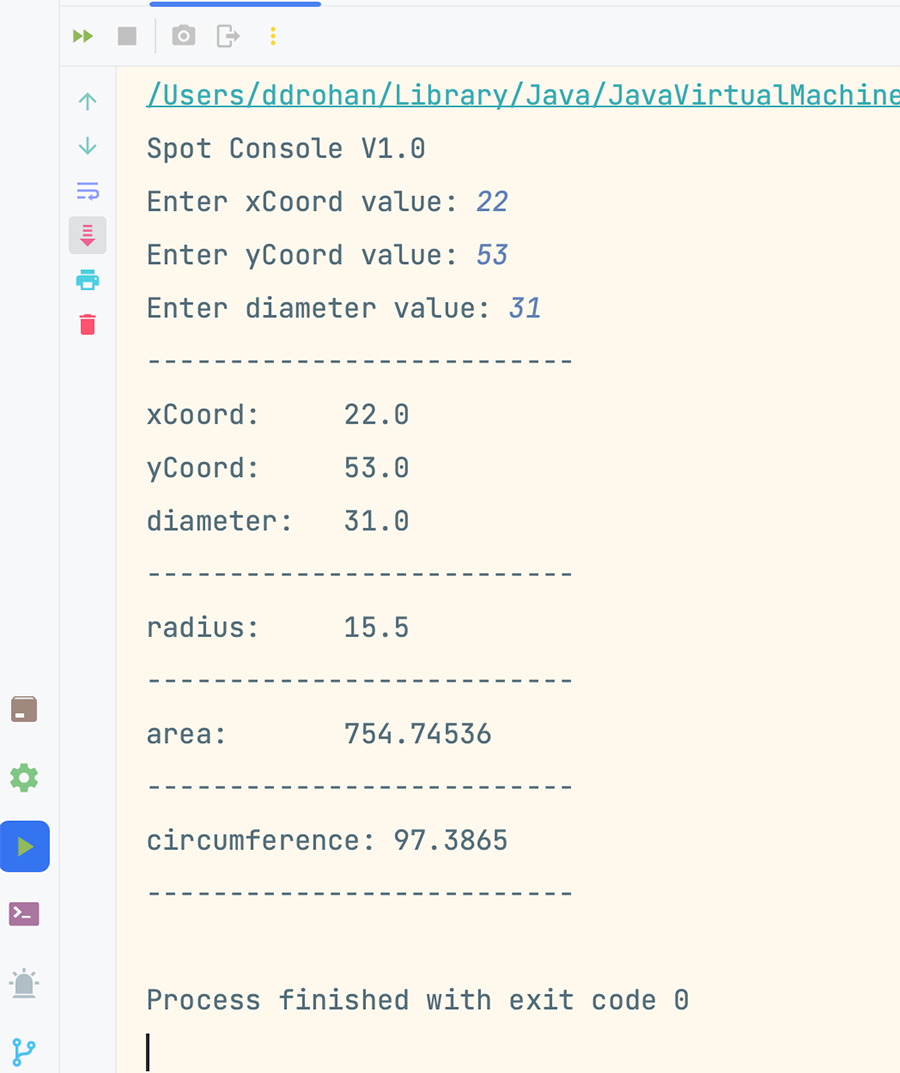
Return back to the code and try figure out what is happening with the reads. We will cover this in more detail next week.
The complete Driver class now looks like this (with a few changes for the UI display)
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Driver {
Spot spot = new Spot(40, 43, 22);
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String args[]) {
System.out.println("Spot Console V1.0");
new Driver();
}
Driver(){
addSpotDetails();
drawSpot();
printRadius();
printArea();
printCircumference();
}
void drawSpot(){
printLine();
System.out.println("xCoord: " + spot.getxCoord());
System.out.println("yCoord: " + spot.getyCoord());
System.out.println("diameter: " + spot.getDiameter());
printLine();
}
void printRadius(){
System.out.println("radius: " + spot.calculateRadius());
printLine();
}
void printArea(){
System.out.println("area: " + spot.calculateArea());
printLine();
}
void printCircumference(){
System.out.println("circumference: " + spot.calculateCircumference());
printLine();
}
void addSpotDetails(){
System.out.print("Enter xCoord value: ");
float enteredXCoord = input.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Enter yCoord value: ");
float enteredYCoord = input.nextFloat();
System.out.print("Enter diameter value: ");
float enteredDiameter = input.nextFloat();
spot = new Spot(enteredXCoord, enteredYCoord, enteredDiameter);
}
void printLine() {
System.out.println("--------------------------" );
}
}