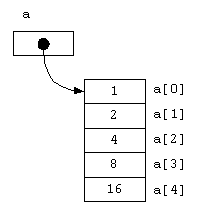
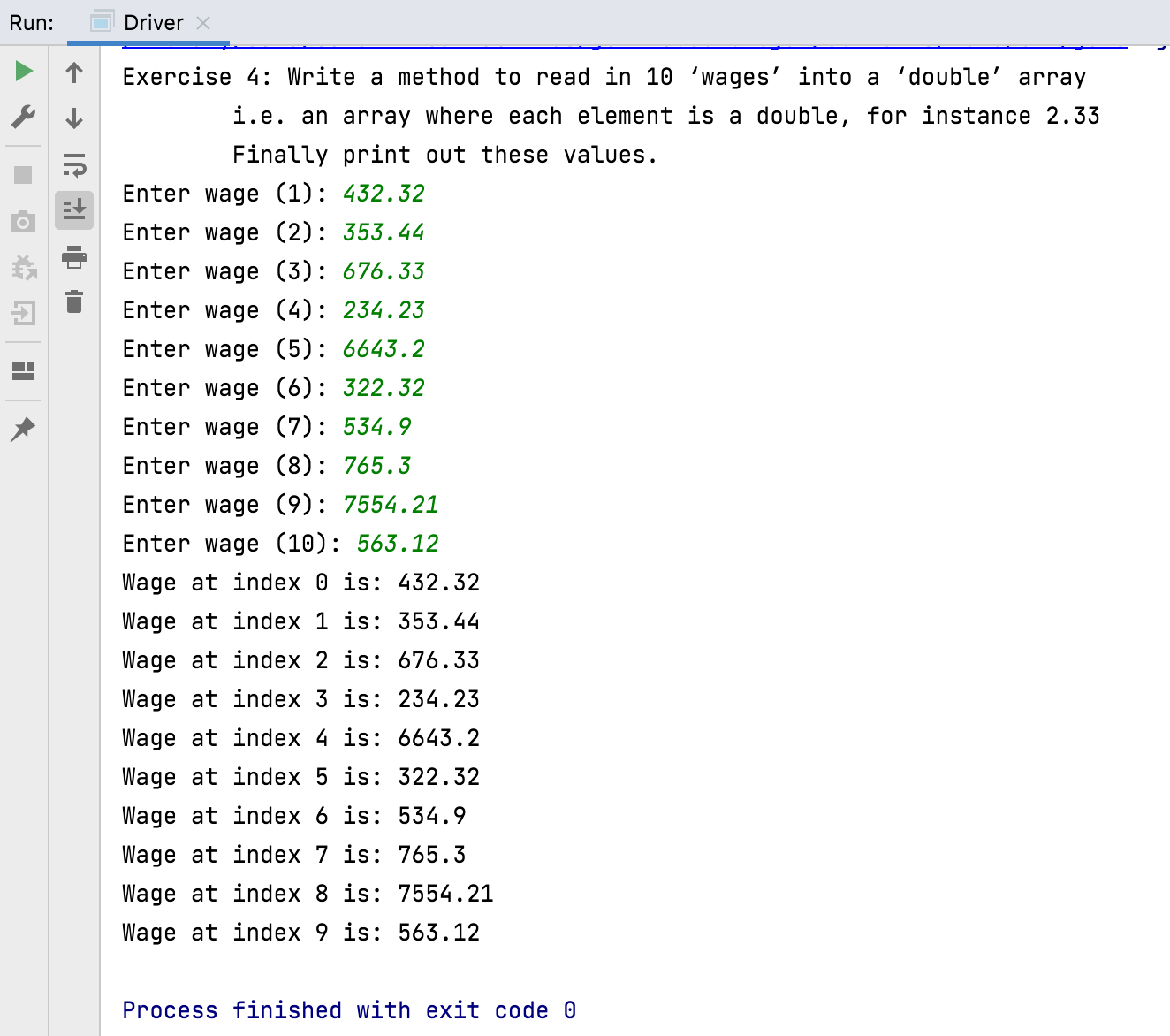
Write a method to read in 10 ‘wages’ into a ‘double’ array (i.e. an array where each element is a double value, for instance 2.33). Finally print out these values. Call this method exercise4.
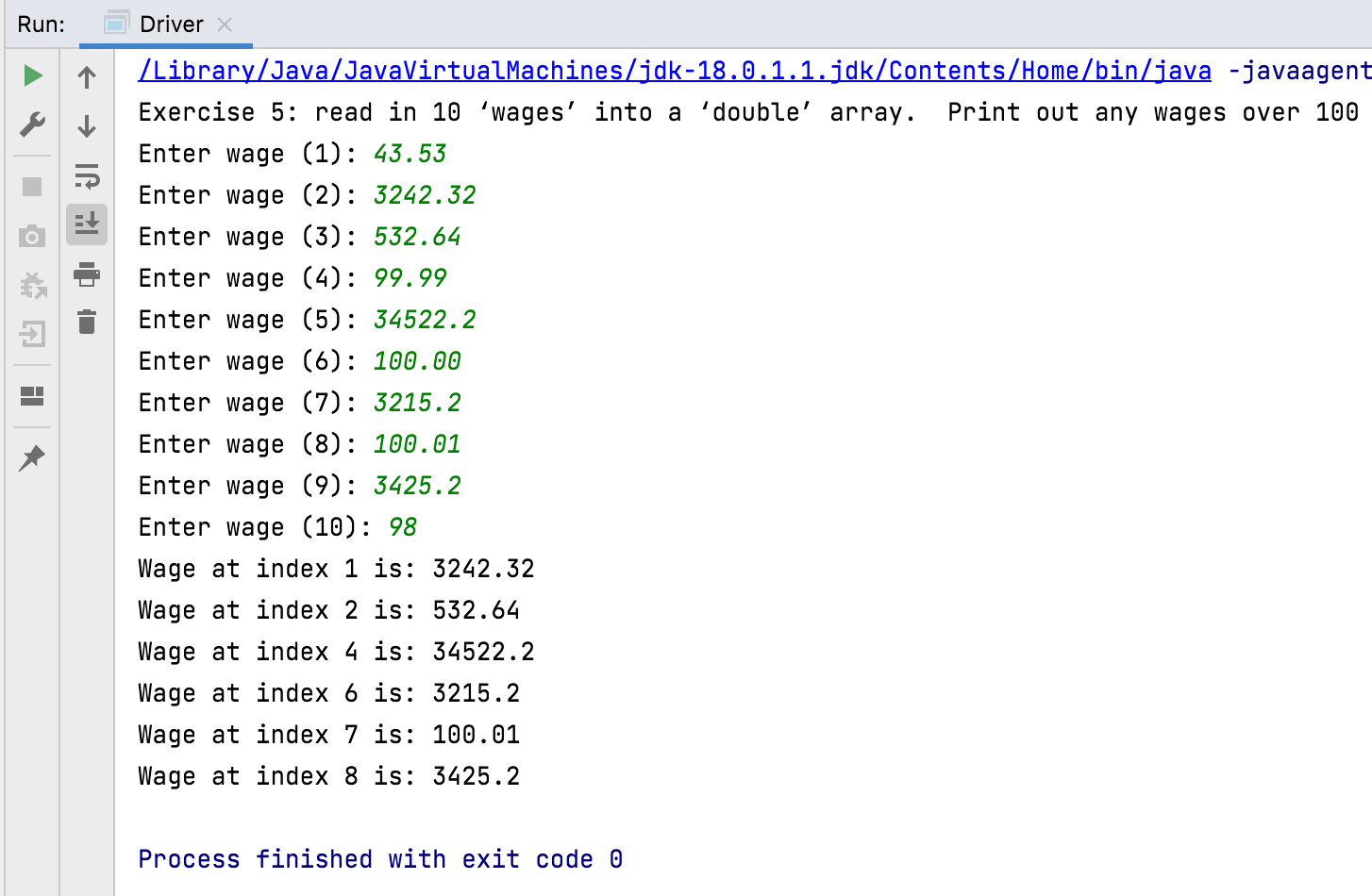
Write a method similar to above , i.e. read in 10 ‘wages’ into a ‘double’ array (i.e. an array where each element is a double, for instance 2.33). This time only print out any wages over 100. Call this exercise5.
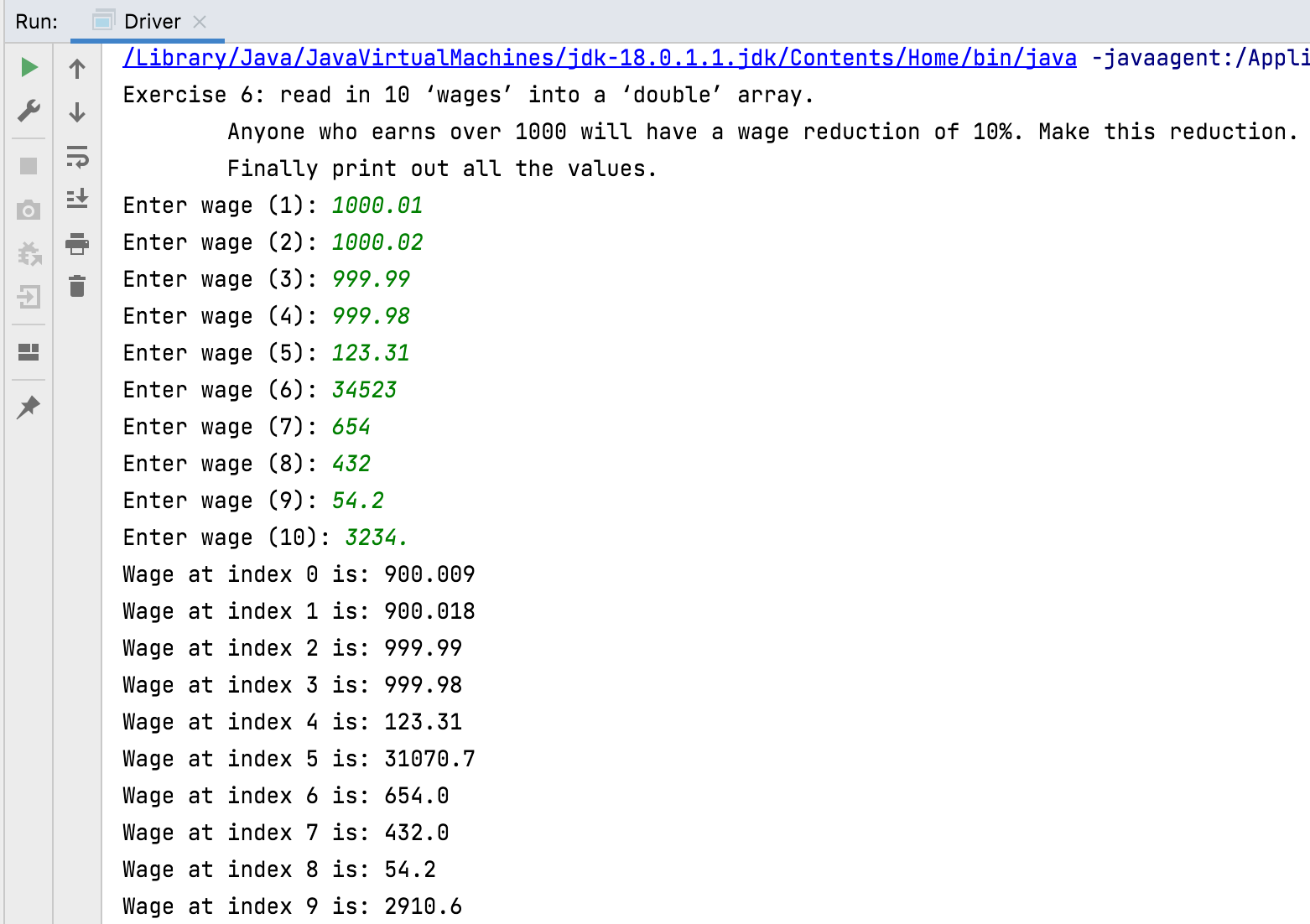
Similar to above, i.e. Read in 10 ‘wages’ into a ‘double’ array (i.e. an array where each element is a double, for instance 2.33). Anyone who earns over 1000 will have a wage deduction of 10%. Make this deduction. Finally print out all the values. Call this method exercise6.
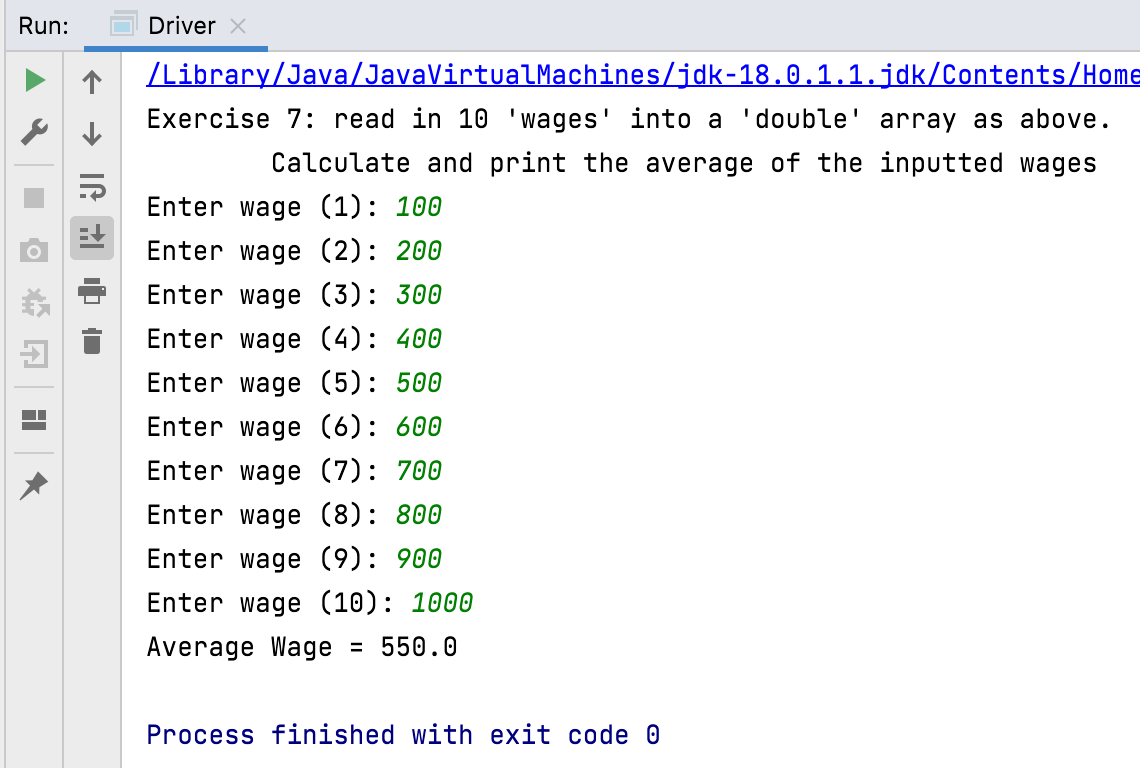
Write a method to read in 10 ‘wages’ into a ‘double’ array as above. Calculate and print the average of the inputted wages. Call this method exercise7.
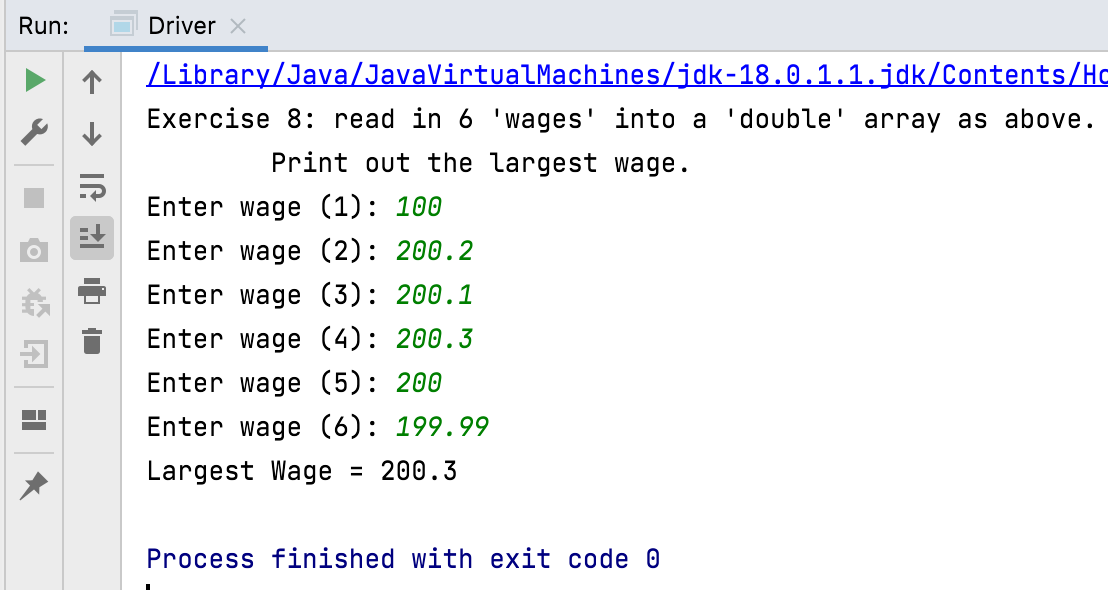
Write a method to read in 6 ‘wages’ into a ‘double’ array as above. Print out the largest wage in the array. Call this method exercise8.
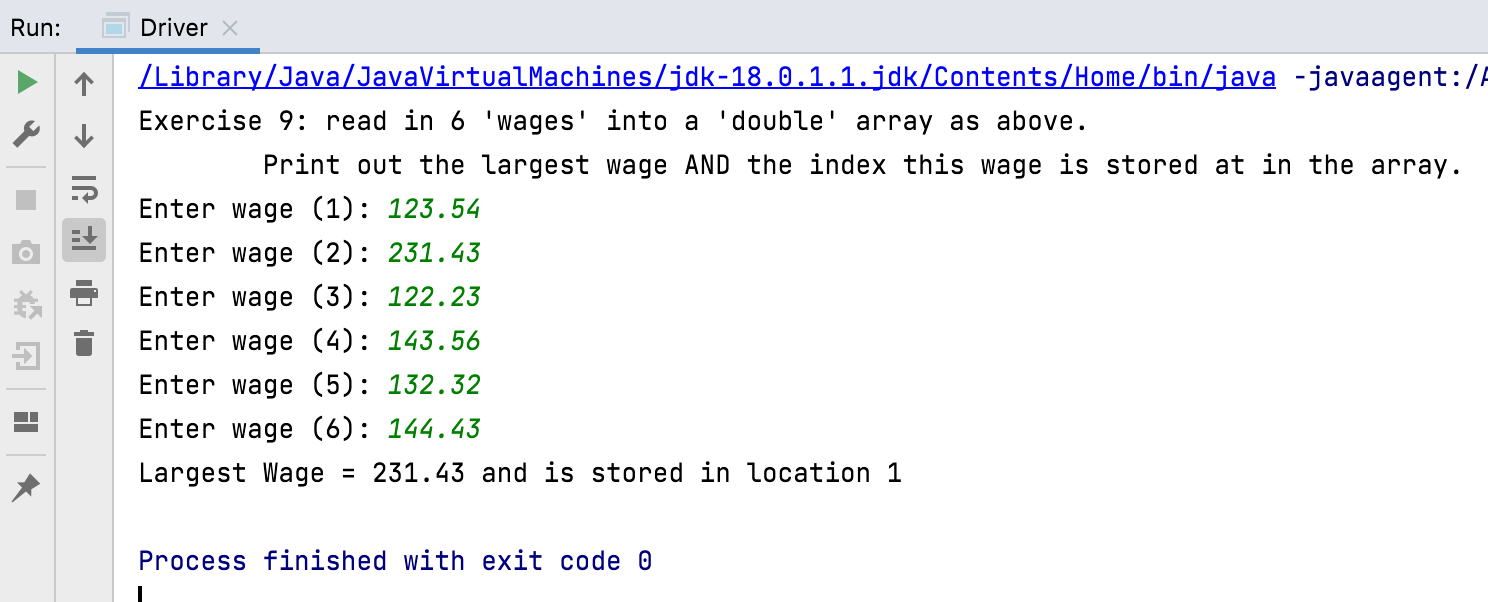
Write a method to read in 6 ‘wages’ into a ‘double’ array as above. Print out the largest wage in the array and the index this wage is stored at in the array. Call this method exercise9.